UV Light Acclimation Capacity of Leaf Photosynthetic and Photochemical Behaviour in Near-isohydric and Anisohydric Grapevines in Hot and Dry Environments
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21548/40-2-3235Abstract
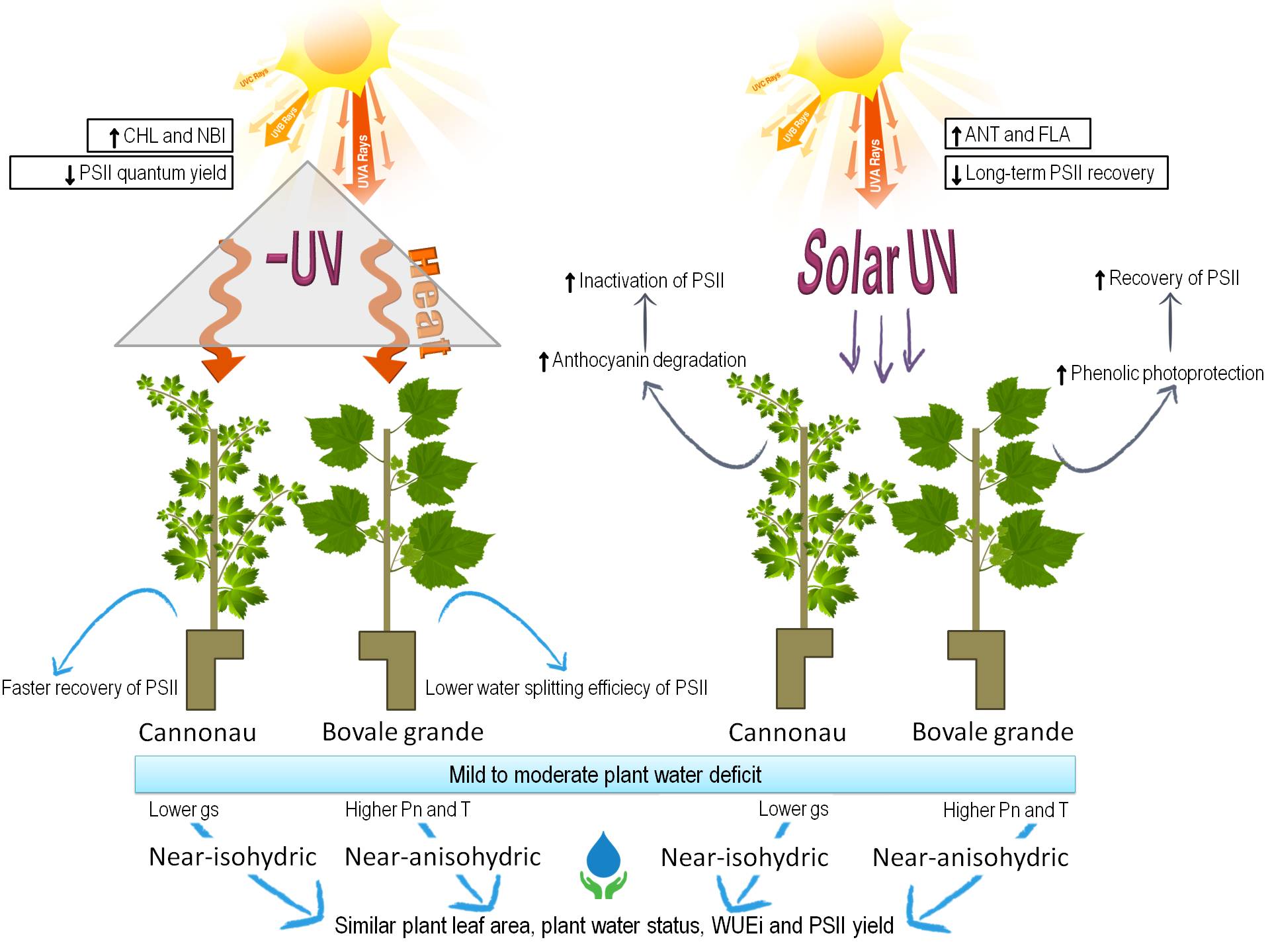
The photosynthetic and photochemical adaptation of grapevine leaves to high UV radiation, under hot and dry summer conditions, was investigated in near-isohydric Cannonau (syn. Grenache) and nearanisohydric Bovale grande (syn. Carignan). From pea-size stage until harvest, vines with mild to moderate water deficit were subjected to UV-blocking treatment (–UV) and compared to a control exposed tosunlight (C). Canopy light and thermal microclimate, growth and density, maximum leaf gas exchange, primary photochemistry (PSII) and phenols were monitored. Average increments in canopy temperature under –UV tunnels during day-time and night-time were 3.3°C and 0.8°C in Bovale grande and 2.6°C and 1.1°C in Cannonau. Cultivars reached similar leaf area, intrinsic water-use efficiency and stem water potential under C and –UV. Cannonau showed lower stomatal conductance, maximum net assimilation and transpiration rates, but also faster recovery of PSII under heat and moderate water stress. UV radiation induced a stronger and longer impact on leaf assimilation, but the duration of elevated temperatures under −UV induced higher photoinhibition and lower photochemical efficiency. A similar degree of correlation between leaf temperature and gas exchange was found among cultivars and treatments. In Cannonau, leaf anthocyanin decreased due to heat-induced long-lasting PSII photoinactivation under C. Conversely, Bovale grande showed higher phenolic content stability, thus higher photoprotection and recovery of PSII functional units. Agronomical practices affecting leaf phenolic accumulation influence canopy acclimation to heat and high sunlight. Vineyard management must avoid excessive canopy sun exposure and duration of elevated temperatures to favour high assimilation, while reducing photoinactivation and heat damage.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
A copyright form will be e-mailed to the corresponding author when the manuscript has been accepted for publication.
In principle, the Author agrees to the following when he/she signes the copyright agreement:
I hereby assign to the SOUTH AFRICAN SOCIETY FOR ENOLOGY AND VITICULTURE (SASEV) the copyright of the text, tables, figures, supplementary material, illustrations and other information (the Material) submitted with the manuscript to be published in SOUTH AFRICAN JOURNAL OF ENOLOGY AND VITICULTURE (SAJEV) (the "Article"). The copyright becomes effective from the date the Article has been accepted for publication in SAJEV.
This is an open access journal, and the authors and journal should be properly acknowledged, when works are cited.
Author's may use the publishers version for teaching purposes, in books, theses, dissertations, conferences and conference papers.
A copy of the authors' publishers version may also be hosted on the following websites:
- Non-commercial personal webpage or blog.
- Institutional webpage.
- Authors Institutional Repository.
The following notice should accompany such a posting on the website: This is an electronic version of an article published in SAJEV, Volume XXX, number XXX, pages XXX - XXX, DOI. Authors should also supply a hyperlink to the original paper or indicate where the original paper (www.journals.ac.za/index.php/sajev/) may be found.
Authors publishers version, affiliated with the Stellenbosch University will be automatically deposited in the University's Institutional Repository SUNScholar.
Articles as a whole, may not be re-published with another journal.
The following license applies:
Attribution CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
